By Mathew Barlow and Jeffrey Basara, UMass Lowell
The heat wave that left more than 100 million people sweating across the eastern U.S. in June 2024 hit so fast and was so extreme that forecasters warned a flash drought could follow across wide parts of the region.
Prolonged high temperatures can quickly dry soils, triggering a rapid onset drought that can affect agriculture, water resources and energy supplies. Many regions under the June heat dome quickly developed abnormally dry conditions.

(NOAA Climate Prediction Center)
The human impacts of the heat wave have also been widespread. In Ohio and Pennsylvania, emergency room visits for heat-related illnesses surged. Several Massachusetts schools without air conditioning closed to protect kids and teachers. In New York and New Jersey, electric wires sagged in the heat, shutting down trains into and out of New York City and leaving commuters stranded.
We study weather patterns involving heat. The June 2024 heat wave was unusually early and long-lasting compared with typical patterns for the Northeast U.S.
It was caused by a large high-pressure system called a heat dome that extended from the ground more than 10 miles up through the atmosphere. A heat dome is both a cause and an effect of extreme heat. Very large and strong heat domes, like the Northeast event – which reached higher into the atmosphere than any previous June event – have a greater potential for higher temperatures impacting more people.
It was also part of a global outbreak of early season heat that put lives at risk in many countries around the world.
Heat is becoming a global problem
Record heat has hit several countries across the Americas, Europe and Asia in 2024. In Mexico and Central America, weeks of persistent heat, with temperatures as high as 125 degrees Fahrenheit (51.8 Celsius), combined with prolonged drought have led to severe water shortages and dozens of deaths.
Extreme heat turned into tragedy in Saudi Arabia as over 1,000 people on the Hajj, a Muslim pilgrimage to Mecca, collapsed and died. Temperatures reached 125 F (51.8 C) at the Grand Mosque in Mecca on June 17.
In Greece, where temperatures were over 100 F (38 C) for several straight days in June, at least several tourists died or were feared dead after going hiking in dangerous heat and humidity.
India also faced temperatures around 120 F (49 C) for days in April and May that affected millions of people, many of them without air conditioning.
The climate connection: This isn’t normal
Although heat waves are a natural part of the climate, the severity and extent of the heat waves so far this year are not “just summer.”
A scientific assessment of the U.S. heat wave estimates that heat this severe and long-lasting was two to four times more likely to occur today because of human-caused climate change than it would have been without it. This conclusion is consistent with the rapid increase over the past several decades in the number of U.S. heat waves and their occurrence outside the peak of summer.
These record heat waves are happening in a climate that’s globally about 2.2 F (1.2 C) warmer than it was before the industrial revolution, when humans began releasing large amounts of greenhouse gas emissions that warm the climate.
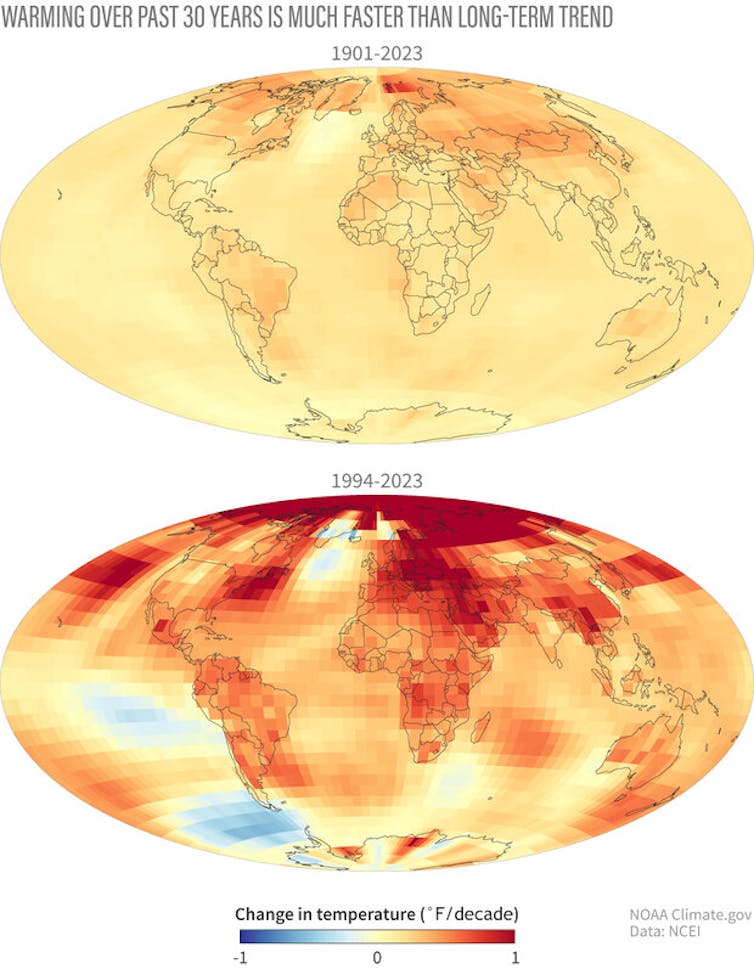
(NOAA NCEI)
While a temperature difference of a degree or two when you walk into a different room might not even be noticeable, even fractions of a degree make a large difference in the global climate.
At the peak of the last ice age, some 20,000 years ago, when the Northeast U.S. was under thousands of feet of ice, the globally averaged temperature was only 10.8 F (6 C) cooler than now. So, it is not surprising that 2.2 F (1.2 C) of warming so far is already rapidly changing the climate.
Countries promised in 2015 as part of the Paris Agreement to keep warming well under 2 C, but current government policies around the world won’t meet those goals. Temperatures are on pace to continue rising, with the increase likely to more than double again by the end of the century.
If you thought this was hot

While this summer is likely be one of the hottest on record, it is important to realize that it may also be one of the coldest summers of the future.
For populations that are especially vulnerable to heat, including young children, older adults and outdoor workers, the risks are even higher. People in lower-income neighborhoods where air conditioning may be unaffordable and renters who often don’t have the same protections for cooling as heating will face increasingly dangerous conditions.
Extreme heat can also affect economies. It can buckle railroad tracks and cause wires to sag, leading to transit delays and disruptions. It can also overload electric systems with high demand and lead to blackouts just when people have the greatest need for cooling.
The good news: There are solutions
Yes, the future in a warming world is daunting. However, countries have made significant progress. In the U.S., the 2022 Inflation Reduction Act has the potential to reduce U.S. greenhouse gas emissions by nearly half by 2035.
Switching air conditioners to heat pumps and network geothermal systems can not only reduce fossil fuel emissions but also provide cooling at a lower cost. The cost of renewable energy continues to plummet, and many countries are increasing policy support and incentives.
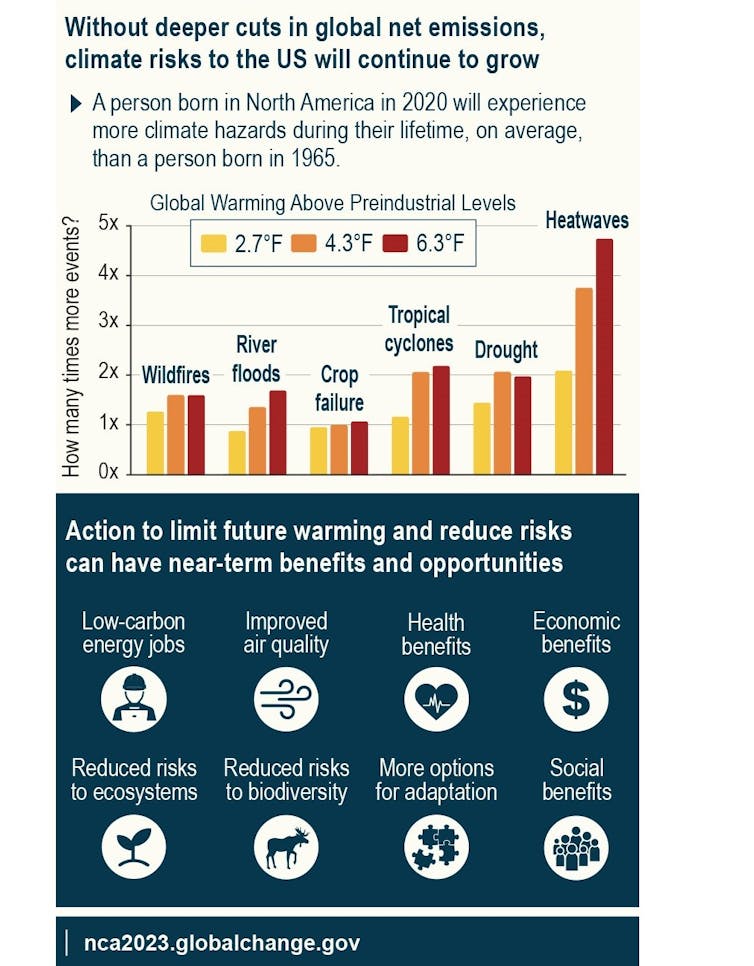
(National Climate Assessment 2023)
There is much that humanity can do to limit future warming if countries, companies and people everywhere act with urgency. Rapidly reducing fossil fuel emissions can help avoid a warmer future with even worse heat waves and droughts, while also providing other benefits, including improving public health, creating jobs and reducing risks to ecosystems.![]()
Mathew Barlow is a professor of climate science and Jeffrey Basara is a professor of meteorology, both at UMass Lowell.
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Sign up for The Invading Sea newsletter by visiting here. If you are interested in submitting an opinion piece to The Invading Sea, email Editor Nathan Crabbe at ncrabbe@fau.edu.



