This article originally appeared on Inside Climate News, a nonprofit, independent news organization that covers climate, energy and the environment. It is republished with permission. Sign up for their newsletter here.
By Amy Green, Inside Climate News
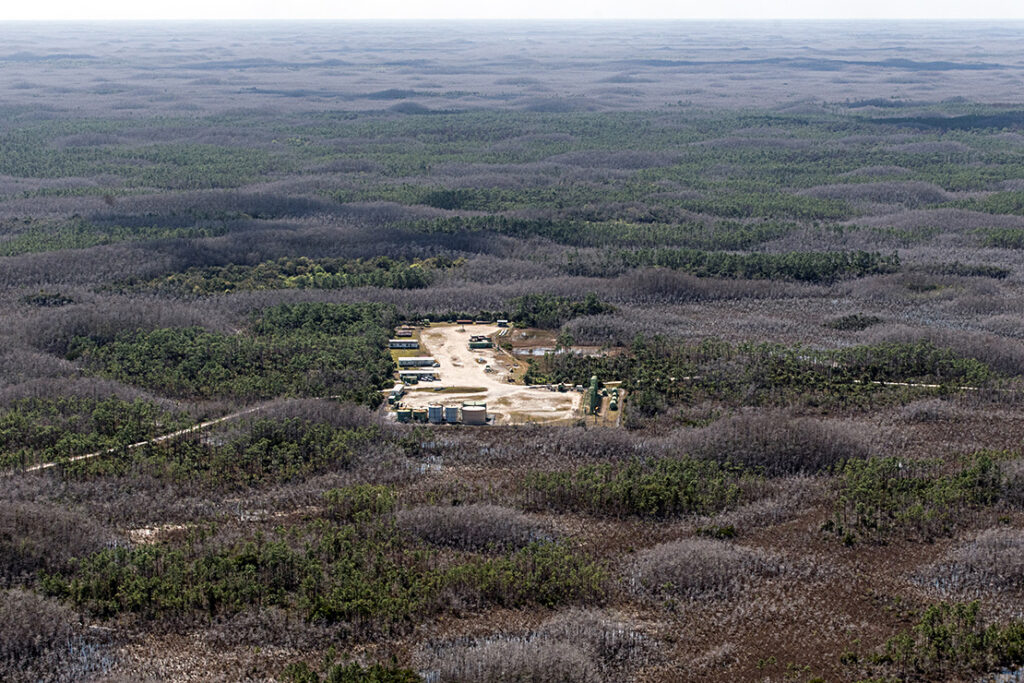
Within a thicket of the Big Cypress National Preserve, established a half-century ago to protect the marshes and sloughs here that make up a vital part of the Florida Everglades, a series of wells extracts oil from more than two miles underground.
The oil field is situated deep within a pine forest of the preserve — the first in the country — which channels more than 40% of the water flowing into Everglades National Park and shelters iconic and imperiled species like the fabled ghost orchid and Florida panther, the official state animal. The wells penetrate thousands of feet beneath an underground aquifer, an important drinking water source, and draw up oil from the so-called Sunniland trend, a reserve stretching across southwest Florida from Miami to Fort Myers, although most of the reserve is situated beneath Big Cypress.
For decades oil production has endured in this corner of the fragile Everglades, a watershed that spans much of the peninsula and is the focus of a $21 billion federal and state restoration effort, one of the most ambitious in human history. Big Cypress is among some 10% of federally protected lands nationwide where the government owns the surface terrain while private entities retain the mineral rights underneath.
“Big Cypress National Preserve is very sacred to us,” said Talbert Cypress, elected chairman of the Miccosukee Tribe of Indians of Florida, a federally recognized tribal nation located in the Everglades. “We have a lot of ceremonial grounds that have been in Big Cypress National Preserve, burial grounds, places where we gather our traditional medicine. So just seeing that sort of damage in a place that really matters to us a lot, it’s sad to see it.”

Now the Miccosukees, longtime environmental stewards in Florida who perhaps most notably helped steer stringent water quality standards for their sacred river of grass, have a plan for phasing out oil drilling within Big Cypress.
The tribe has joined with WildLandscapes International, a nonprofit land conservation group, to engineer a multi-million-dollar deal with the Collier family, which owns the vast majority of the mineral rights beneath the preserve. If the agreement is finalized, the family would give up the mineral rights associated with some 465,000 acres to the federal government.
“Unfortunately I cannot share. It’s under a non-disclosure,” said David Houghton, director of WildLandscapes International, when asked about the details. “The deal includes all the lands that the Colliers own the mineral rights on, minus what they currently have under lease.”
The proposal comes amid interest in expanding oil exploration and development within Big Cypress, even as rising global temperatures associated with fossil fuel emissions represent yet another threat to the Everglades, a watershed responsible for the drinking water of some 9 million Floridians. Most recently a Texas oil and gas company submitted a permit application to the National Park Service for two new sites within the preserve.
“We think we’ve got a deal here. We don’t know that, but we think,” Houghton said. “We’ll get a number, and that number either will work or it won’t—and I think it will.”
Liquid tar
The Everglades are Florida’s most important freshwater resource. The watershed spans central and south Florida, encompassing the Kissimmee River, Lake Okeechobee, sawgrass prairies to the south and Florida Bay. It includes several federal- and state-protected lands including the Everglades Headwaters National Wildlife Refuge, Florida Panther National Wildlife Refuge, Big Cypress National Preserve and Everglades National Park. Various efforts over the last century to drain the Everglades, the largest steered by the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, have made modern Florida possible and left the river of grass drastically altered.
The Humble Oil and Refining Company, a predecessor of ExxonMobil, discovered oil in Southwest Florida in 1943, after the governor and cabinet at the time offered a $50,000 reward to those who first found oil in the state.
Today Florida is responsible for less than 0.04% of the nation’s oil production, according to a report the Conservation Economics Institute, a nonprofit research organization, prepared for the Natural Resources Defense Council. The industry employs fewer than a thousand members of the state’s workforce and accounts for $25.4 million or 0.0002% of its gross domestic product. A separate study by the American Petroleum Institute concluded the oil and natural gas industry contributes nearly $22.1 billion to the Florida economy and supports nearly 266,800 jobs.
The vast majority of the state’s oil production occurs in the Panhandle, according to the Conservation Economics report. The two oil fields within Big Cypress, Bear Island and Raccoon Point, together were responsible for 585 barrels a day in 2020, about one-seventh of the state’s daily total. Oil was discovered at Bear Island, which is located partially within the preserve, in 1972, before the preserve was established, and production began a year later. At Raccoon Point, southeast of Bear Island, oil was detected in 1978. Production began in 1981, and the field was expanded in 1992.
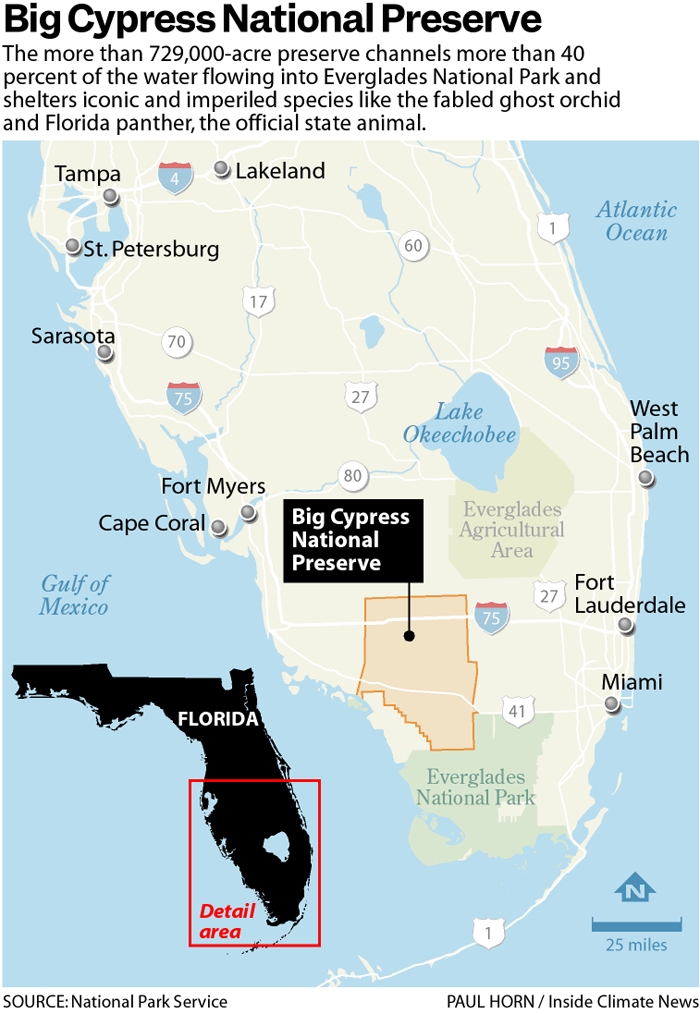
Big Cypress was established in 1974. Two years later the Collier family, for whom Collier County, where a large portion of the preserve is situated, is named, conveyed 76,790 acres to the National Park Service to help create the preserve, with the family maintaining the underground mineral rights. The Colliers can trace their family tree to the early 20th century advertising magnate Barron Gift Collier, at the time the largest landowner in Florida. In 1996 the family conveyed an additional 83,000 acres to the National Park Service to expand Big Cypress. Today Big Cypress encompasses more than 700,000 acres, including much of the western Everglades.
In 2003 the federal government agreed to purchase the Colliers’ mineral rights for $120 million, but the purchase fell through. At the time various appraisals valued their mineral rights beneath Big Cypress, the Florida Panther National Wildlife Refuge and Ten Thousand Islands National Wildlife Refuge at between $5 million and $475 million.
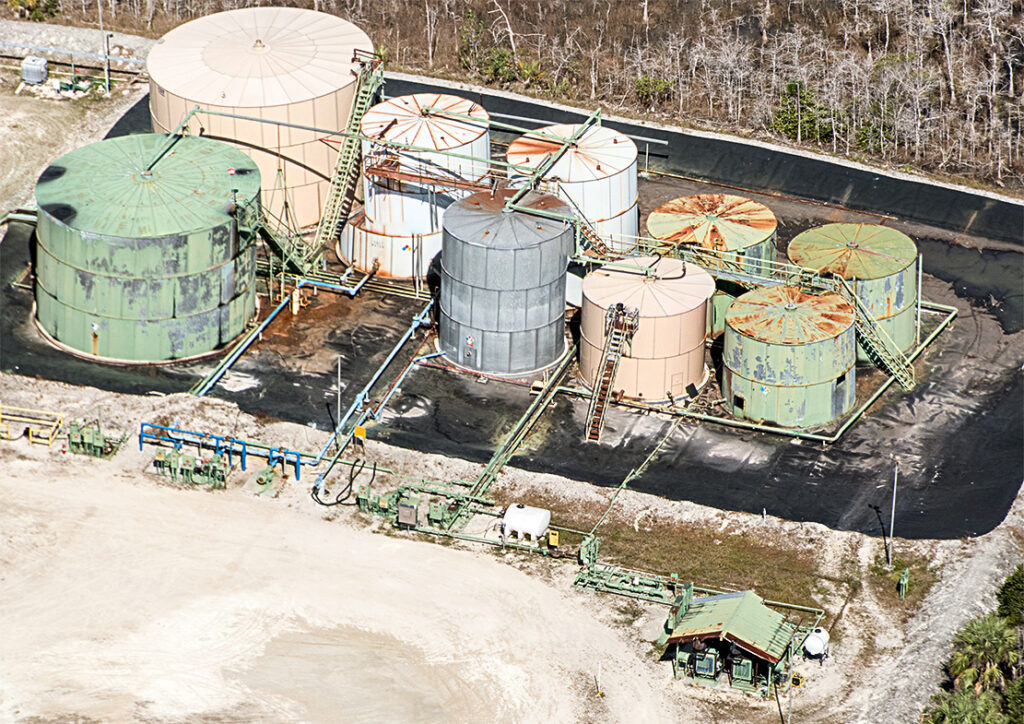
The oil here is of the heavy-sour variety, with a consistency of liquid tar, according to a website of the Collier Resources Company, which manages the family’s mineral holdings. When refined, the oil is used in auto, aviation and diesel fuels, lube oils and asphalt. Edward Glab, director of the Global Energy Security Forum in the School of International and Public Affairs at Florida International University, characterized the oil as not high-grade or worth a lot of money. Multiple phone calls to the Collier Resources Company were not returned.
“To me it makes no sense drilling for oil anywhere in the Everglades,” Glab said. “It just doesn’t because the reserves are simply not going to be there to justify that sort of investment.”
“It’s a lot of trouble for something that’s not producing a ton of oil, and it’s not like premium-grade oil. It’s like machinery oil, the kind used for heavy machinery,” said Cypress, chairman of the Miccosukee Tribe of Indians of Florida. “For us when we see the amount of work that goes into the extraction, the damage that they do, it doesn’t seem worth it.”
Acidizing rather than fracking is more likely to be used in Florida to extract oil because of the state’s geology, which is characterized by porous limestone that harbors underground aquifers, according to the Conservation Economics report. Acidizing involves injecting the oil-bearing rock formations with a mixture of acid, water and other chemicals, dissolving the formations and allowing the oil to flow more easily to the well. Some 93% of the state’s population depends on groundwater for drinking water, far more than any other state in the nation.
Wastewater from such techniques can contain pollutants and threaten the groundwater, although the Collier family says multiple precautions are taken throughout the drilling process to protect the sensitive environment here, according to the Collier Resources Company website. For instance, to safeguard the aquifers a series of steel casings and thick layer of cement surround all oil-producing wells. At the well sites a limestone pad is constructed with a berm around it to prevent stormwater runoff from carrying pollutants into the environment. The pads also include a liner to protect the groundwater. The Collier family website also says water sampling has revealed no evidence of groundwater contamination.
But spills have occurred. A spill at Raccoon Point in October 2018, caused by corrosion in a production well, released 2,000 gallons of wastewater mixed with oil. The operator at the time, under lease with the Collier family, said the fluids stayed within a bermed area, and most of the fluids were recovered, according to a Florida Department of Environmental Protection report.
“There’s just so many potential damages that can happen here, and when it’s such a small amount of oil that’s being produced it does not make economic sense,” said Evan E. Hjerpe, executive director of the Conservation Economics Institute and author of the report. “It’s kind of an antiquated or artifact of previous times, and it would benefit the public much greater to move forward without having these potential risks going on.”
‘The reason we survived‘
For hundreds of years the Miccosukee people hunted, fished and held religious ceremonies among the soaring cypress swamps and sweeping sawgrass prairies of Big Cypress. During the First and Second Seminole Wars, in the first half of the 19th century, they were pushed deep within the watery wilderness and found sanctuary on the tree islands scattered here.
“We have a mother-child relationship with the Everglades because it helped us survive the removal era as well as the termination era, and so without it we would not exist as a sovereign entity. We would have either been annihilated or removed to the West,” said Curtis Osceola, chief of staff for the Miccosukee Tribe of Indians of Florida. “Our land is the reason we survived. It is the reason why we’re here, and so we have a duty to the land that once protected us. And so that’s what it is to be Miccosukee, is to serve and protect the lands of our environment.”
Today most of the 600-member tribe lives on tribal lands within Everglades National Park, although some 100 to 200 Miccosukees, members of the Seminole Tribe of Florida and other native people of Miccosukee and Seminole heritage live in 15 villages within Big Cypress. About eight of the communities, as well as a school, are situated downstream from Raccoon Point, raising concerns that spilled oil could flow in their direction, affecting surface water and the underground aquifer, which some residents have tapped with residential wells. Osceola said back when Big Cypress was established and the Collier family maintained the underground mineral rights, the Miccosukees were left out of the negotiations.
“Part of our culture tells us that the land should rest, and those fluids beneath the land should go undisturbed. That includes natural gas, oil, things like that,” he said. “So the extraction of oil is a very unnatural act.”

Oil drilling within Big Cypress is the latest environmental issue the tribe has taken up. After the federal government sued the state in the 1980s over water pollution in Everglades National Park and the Arthur R. Marshall Loxahatchee National Wildlife Refuge, the Miccosukees got involved in the issue as defenders of the river of grass. The litigation led to a monumental state cleanup effort, which remains in progress today.
The tribe’s pending deal with the Colliers would halt all future drilling within Big Cypress, although existing production could continue at least for now. The agreement likely would upend a plan for two new sites in Big Cypress that Burnett Oil Co., Inc., an oil and gas company based in Fort Worth, Texas, is pursuing.
In 2017 and 2018, Burnett, under a lease with the Collier family, conducted an off-road seismic survey of 110 square miles of Big Cypress. The survey involved applying vibrating plates to the ground and sending seismic signals deep beneath the surface to map potential oil. To access the remote area, 33-ton vibroseis trucks were used. The hefty vehicles sank into the soft, water-soaked soils, leaving deep ruts, consequential in an ecosystem where the boundary between land and water is blurred and inches of elevation can mean vast differences in habitat. The effort also harmed slow-growing mature dwarf cypress trees. As many as 500 of the trees were cut down to allow the trucks to move through the area, according to a 2023 report by the National Parks Conservation Association.
“This would be creating brand new fossil fuel infrastructure in a time where we need to be transitioning away from that.”
Six years later the landscape has not recovered, the report said. The survey left lasting scars including soil compaction and deep twisting furrows, and almost none of the felled cypress trees has shown signs of regrowth. The National Parks Conservation Association wants the National Park Service to compel Burnett to replant the trees and address the other problems. Burnett did not respond to multiple requests for comment.
The two new sites Burnett is proposing would be similar to that at Raccoon Point, according to the company’s permit application to the National Park Service. The document said the project is designed to minimize environmental impacts and avoid historical, cultural and archeological resources, including Miccosukee and Seminole areas.
If the National Park Service were to approve Burnett’s plan, that would contradict the Biden administration’s demonstrated commitment to confront climate change, said Christina Reichert, senior attorney in the Florida office of Earthjustice, a nonprofit litigating environmental issues.
“It doesn’t match up to the promises that we’re hearing and the focus that this administration should be having on fighting the climate crisis. This would be creating brand new fossil fuel infrastructure in a time where we need to be transitioning away from that,” she said. “Wetlands are carbon sinks. One of the things they do is absorb carbon from the atmosphere and store it. So it doesn’t make sense to destroy wetlands and then build fossil fuel infrastructure.”
Hjerpe of the Conservation Economics Institute said closing an oil well can be difficult and costly, sometimes making it more advantageous to continue operating the well even when the oil is not of the highest quality. He said it is possible Burnett’s lease agreement with the Collier family mandated exploration plans or focused on increasing new development.
“When you see the path forward, and there’s certainly potential for a buy-out of your minerals and buy-out of your operations, then it completely makes financial sense to make sure that you are heavily invested in the area and that you keep producing and illustrating the value and increasing the value of your operations,” he said.
Next steps
Climate change associated with fossil fuel emissions is poised to have a big impact on the Everglades. Rising temperatures will increase evaporation, stressing the watershed that already is pressured by explosive population growth and development. The hotter temperatures also will lead to precipitation changes, raising concerns about whether the water management infrastructure here, some of the most complex in the world, is up to future challenges.
The agreement involving the Miccosukees, Colliers and WildLandscapes International includes three phases. Under the first phase, completed last year, the Collier family sold 11,141 acres including the mineral rights, to the Florida Department of Environmental Protection and South Florida Water Management District. The second phase, focused on the mineral rights beneath Big Cypress, still faces several steps, said Houghton of WildLandscapes International.
“The way the deal is set up we have a floor value, and if the appraisal meets that or above then the Colliers are obligated to sell,” he said. “If the appraisal is below, the Colliers could get out.”
If the agreement moves forward, Congress would appropriate the funding, which could take a few more years. The money would come from the Land and Water Conservation Fund, a federal program that puts earnings from offshore oil and gas leasing toward land conservation. The third phase involves land near Everglades City, a small town outside of Big Cypress.
Cypress, chairman of the Miccosukee Tribe of Indians of Florida, said future plans go further. Eventually the tribe wants to stop all oil drilling within Big Cypress for good.
“Florida is going to need more freshwater, more drinking water, and we don’t have that without the Everglades,” he said. “It matters to everybody in Florida.”
Amy Green covers the environment and climate change from Orlando, Florida. She is a mid-career journalist and author whose extensive reporting on the Everglades is featured in the book “Moving Water,” published by Johns Hopkins University Press, and podcast “Drained,” available wherever you get your podcasts. Amy’s work has been recognized with many awards, including a prestigious Edward R. Murrow Award and Public Media Journalists Association award.
This story was produced in partnership with the Florida Climate Reporting Network, a multi-newsroom initiative founded by the Miami Herald, the South Florida Sun Sentinel, The Palm Beach Post, the Orlando Sentinel, WLRN Public Media and the Tampa Bay Times.
Sign up for The Invading Sea newsletter by visiting here. If you are interested in submitting an opinion piece to The Invading Sea, email Editor Nathan Crabbe at ncrabbe@fau.edu.



